Introduction and Workflow
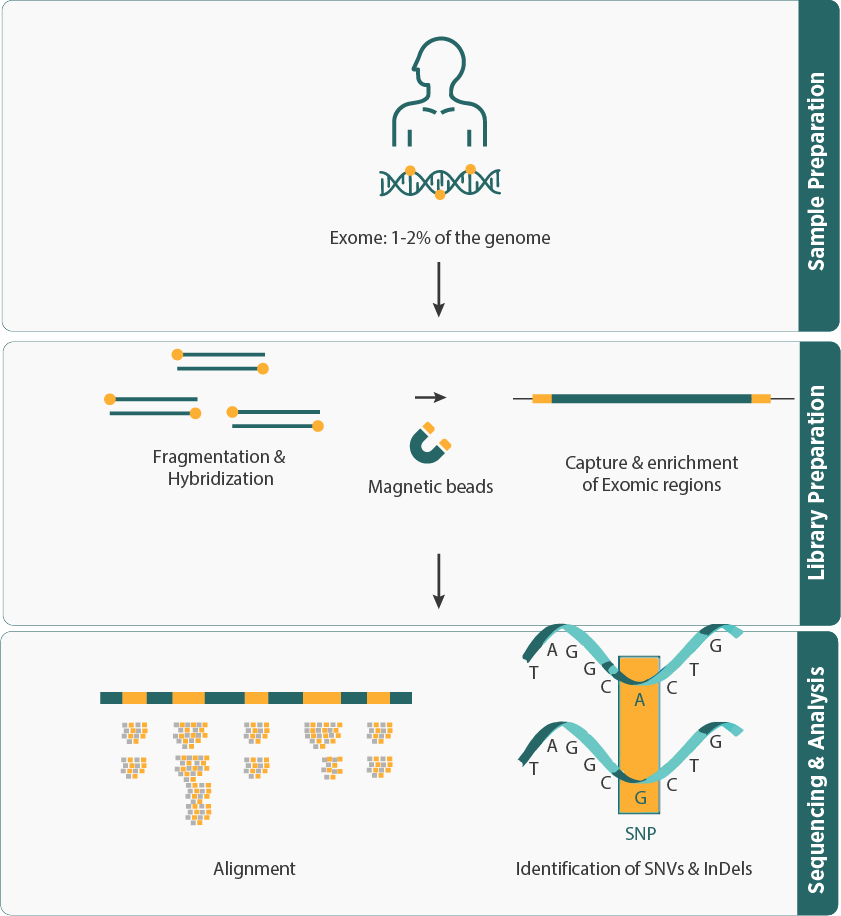
- Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) is sequencing of only protein-coding regions (<2% of the genome, also known as exome), which accounts for 80-85% of disease-related variants.
- The workflow involves DNA isolation, fragmentation, capturing exonic regions, and sequencing to generate millions of short reads. In the bioinformatics analysis, these reads undergo alignment to a reference genome, followed by the variant calling (SNVs, Indels) and data analysis.
- Pinpoints potential disease-causing mutations, providing valuable insights for population genetics, genetic disease research, and cancer studies.
- Extensively utilized in diagnostic setting to detect clinically relevant genomic alterations associated with phenotype of the patient.
Advantage
- Cost-effective as compared to Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS), making it accessible to a broader range of researchers and clinicians.
- WES offers extensive sequencing of exonic regions, improving the detection of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), copy number variants (CNVs), and insertions/deletions (InDels) with a sensitivity comparable to WGS, ensuring high accuracy in identifying genetic variants.
- WES generates a smaller data set compared to WGS, facilitating faster and easier data analysis, which can expedite research and diagnostic processes.
- WES is widely used in both medical and agricultural fields, supporting advancements in disease diagnosis, personalized medicine, and crop improvement. Provides a comprehensive, high-resolution view of the genome, surpassing the coverage offered by targeted sequencing.
Applications of Whole Exome Sequencing
- Genetic Disorder Diagnosis- Identifies genetic mutations associated with rare and inherited disorders by focusing on the exonic regions where most disease-related variants occur. This enables accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
- Cancer Research- Detects somatic mutations in cancer genomes, providing insights into tumor biology, identifying potential biomarkers for early detection, and guiding targeted therapies for more effective treatment.
- Drug Development- Assists in the discovery of new drug targets and the development of precision medicine by revealing the genetic underpinnings of diseases and how genetic variations affect drug responses.
- Population Genetics- Explores genetic variations in diverse populations to understand genetic diversity, evolutionary processes, and the genetic basis of complex traits and diseases, aiding in public health and epidemiological studies.
- Functional Genomics- Provides insights into gene function and regulation by identifying coding mutations that impact protein function, contributing to our understanding of gene-disease relationships and mechanisms of gene action.
- Plant Genomics- Supports crop improvement and plant breeding programs by revealing the genetic basis of desirable traits and enhancing the understanding of plant genomes.
Service Specifications
Sample Requirement
• Genomic DNA
• Cultivated cells, Blood, tissues, Fresh Frozen, FFPE(formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded)
Please refer to sample submission guidelines or Contact Us!
Sequencing Platform
Illumina NovaSeq 6000/ NovaSeq X

Deliverables
- The original sequencing data
- Experimental results
- Bioinformatics and Data Analysis Report
- Details in Whole Exome Sequencing (customizable)
