mRNA Sequencing
Introduction and Workflow
- Messenger RNA-Seq (mRNA-Seq) is a focused RNA-Seq method that targets polyadenylated (poly-A) transcripts, which comprise only about 1-2% of the transcriptome, mainly representing coding genes. By enriching these poly-A-tailed RNAs, mRNA-Seq offers a precise snapshot of gene expression, capturing the complete range of mRNA transcripts within a sample and enabling detailed analysis of gene activity across various conditions.
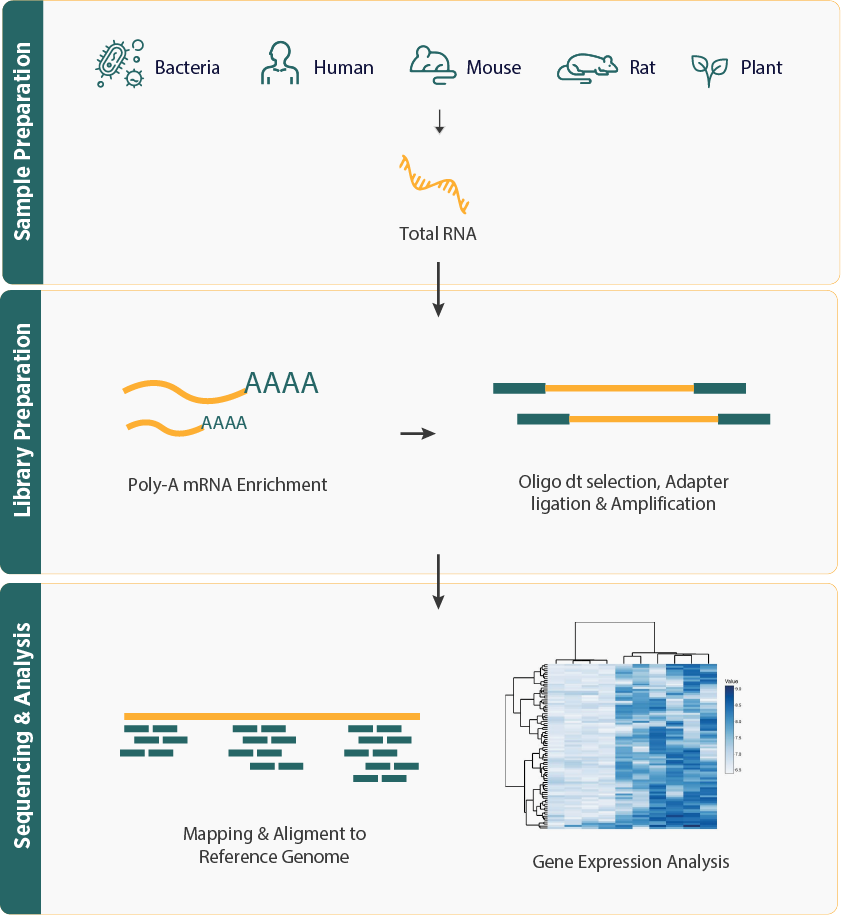
- mRNA-seq workflow typically includes RNA extraction, enrichment or depletion of mRNA, library preparation, and high-throughput sequencing. This workflow ensures precise and efficient capture of mRNA transcripts for thorough downstream analysis.
- Bioinformatics analysis for mRNA-seq involves several key steps: data preprocessing, alignment to a reference genome, quantifying gene expression levels, and advanced downstream analyses such as differential expression, pathway enrichment, and gene ontology analysis.
- Widely applicable across diverse research fields, including human, animal, and plant studies, providing profound insights into genetic landscapes and contributing to our understanding of gene function and regulation.
Advantage
- mRNA-Seq provides a targeted analysis of gene expression specific to protein-coding regions, making it ideal for studies focused on gene regulation, protein synthesis, and disease-related expression changes.
- mRNA-Seq focuses on mRNA enrichment, which minimizes the impact of non-coding RNAs and enhances sensitivity for detecting gene expression changes.
- Focusing solely on coding regions, mRNA-Seq does not require rRNA-specific probes (Costly) for ribosomal RNA removal and requires comparatively lesser data, making it a more cost-effective alternative to Whole Transcriptome Sequencing.
- With a more targeted dataset, the bioinformatics analysis of mRNA-Seq is often simpler and faster, focusing on coding genes without the complexity introduced by non-coding RNAs.
Bioinformatics Pipeline

Applications of mRNA Sequencing
- mRNA sequencing is widely utilized across plants, animals, microbes, and humans.
- Developmental Biology- Studies gene expression patterns during different stages of development, helping to unravel the mechanisms of cell differentiation and tissue formation.
- Disease Mechanisms- Uncovers mRNA expression profiles associated with various diseases, including genetic disorders and autoimmune conditions, to identify potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.
- Drug Discovery- Analyzes mRNA expression changes in response to drug treatments, providing insights into drug mechanisms of action and helping to identify potential drug candidates.
- Functional Genomics- Provides a comprehensive view of gene expression across different conditions, facilitating the study of gene functions and regulatory networks.
- Comparative Genomics- Compares mRNA expression profiles across different species or environmental conditions to understand evolutionary differences and functional conservation.
- Toxicology- Assesses changes in gene expression in response to toxic substances, aiding in the identification of biomarkers for toxicity and understanding the impact of chemicals on biological systems.
Service Specifications
Sample Requirement
Total RNA ≥ 2 μg, Minimum Quantity: 500 ng, Concentration≥ 50 ng/µL
Cells, Tissue and other samples
Please refer to sample submission guidelines or Contact Us!
Sequencing Platform
Illumina NovaSeq 6000/ NovaSeq X

Deliverables
- The original sequencing data
- Experimental results
- Bioinformatics and Data analysis report
- Details of mRNA Sequencing (customizable)
