Circular RNA Sequencing
Introduction and Workflow
- Circular RNA sequencing (circRNA-seq) focuses on identifying and characterizing non-coding circular RNAs formed through back-splicing events. These circRNAs regulate gene expression by acting as miRNA sponges, influence alternative splicing, modulate transcription, interact with proteins, and serve as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
- As compared to Linear RNAs, circRNAs are covalently closed loops with no free ends, which provides them with enhanced stability and distinct regulatory functions in gene expression and cellular processes.
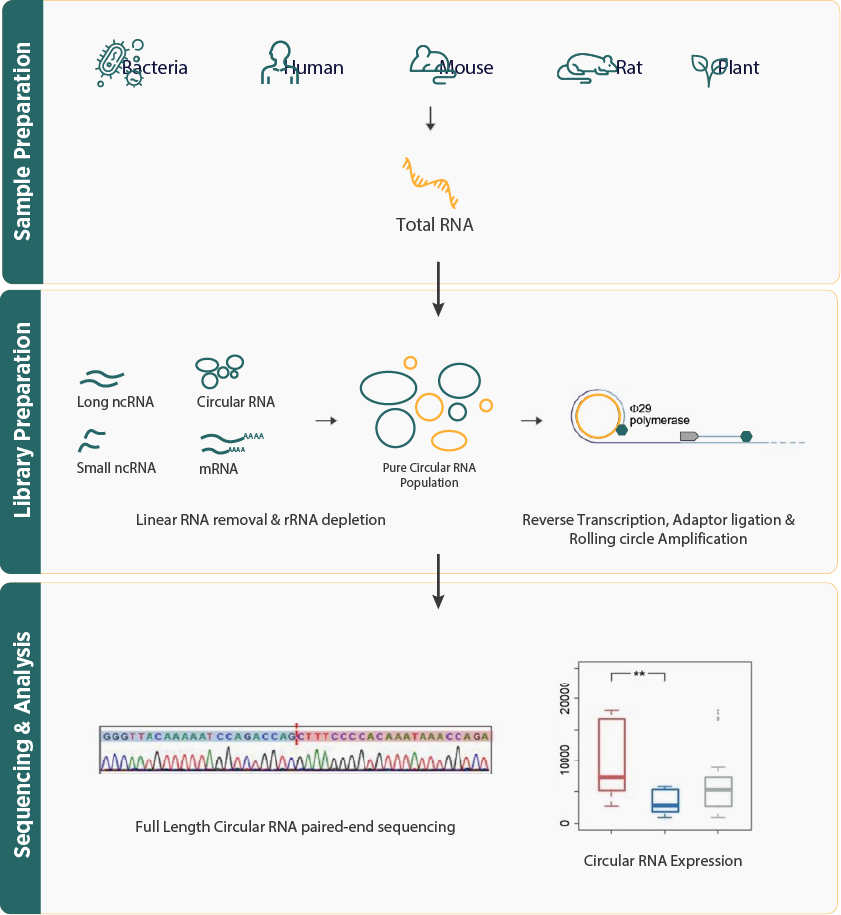
- The workflow starts with isolating total RNA from the sample, which includes both linear and circular RNAs. Linear RNAs are then removed through ribosomal RNA (rRNA) depletion or exonuclease treatment to enrich the circular RNA fraction. Next, the RNA is circularized, and sequencing adapters are added during library preparation. The final step involves sequencing the prepared libraries.
- Bioinformatics analysis for circRNA sequencing involves preprocessing data and mapping reads to a reference genome to identify back-splicing junctions. Computational tools are then used to quantify circRNA expression, discover novel circRNAs, and perform downstream analysis.
Advantage
- Circular RNAs are inherently more stable due to their covalently closed structure, making them less susceptible to degradation and providing reliable expression data.
- Enables the identification of novel isoforms and splice variants that may not be detected with traditional RNA sequencing methods.
- Offers a detailed view of circular RNA expression and their interactions within the cell, aiding in a deeper understanding of gene regulation and cellular processes.
- Closed-loop structure of circRNAs minimizes potential sequencing artifacts, leading to more accurate and consistent data.
Bioinformatics Pipeline

Applications of Circular RNA Sequencing
- Circular RNA sequencing is widely utilized across plants, animals, and humans.
- Therapeutic Targets for Cancer- Small molecules or antisense oligonucleotides can be used to modulate circRNA activity. Consequently, targeting oncogenic circRNAs could provide novel strategies for inhibiting tumor growth.
- Developmental Biology- Investigates circRNA roles in developmental processes and differentiation, enhancing understanding of gene regulation during growth and development.
- Disease Biomarkers- circRNAs are stable in body fluids such as blood and saliva, and exhibit altered expression in conditions like cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological diseases. This stability and variation in expression patterns suggest their potential as biomarkers for these diseases.
- Functional Studies- Functional studies can involve manipulating circRNA levels in cell models through techniques such as knockdown or CRISPR/Cas9, to investigate their roles in cellular processes.
Service Specifications
Sample Requirement
Total RNA amount: ≥ 2.0 μg, Blood and other samples
Please refer to sample submission guidelines or Contact Us!
Sequencing Platform
Illumina NovaSeq 6000/ NovaSeq X

Deliverables
- The original sequencing data
- Experimental results
- Bioinformatics and Data Analysis Report
- Details of Circular RNA Sequencing (customizable)
